To propagate trees, grafting is an essential technique. This process not only increases the number of varieties on a tree but also helps address branch damage and improve fruit quality. Here’s a guide on how to graft trees correctly.
When to Graft
Grafting can be done in early April, before the sap starts to move, or in May, when the sap is flowing. Different grafting methods can be employed during these times.
Preparing for Grafting
- Harvest Cuttings: Cuttings should be taken from healthy, one-year-old shoots with three developed buds. This can be done in the autumn or spring.
- Storage of Cuttings: Store cuttings by tying them in bundles and placing them in wet sand in a basement, or bury them in soil. Ensure the cut ends are treated with garden boil to protect them.
- Winter Protection: Bury cuttings in snow on the north side. As spring approaches, cover them with peat, manure, and plywood.
- Wrapping: Treat cuttings with garden compost and wrap them with spruce branches, roofing felt, or tulle to prevent mold and rodent damage.
Understanding Grafting Components
- Scion: The cutting being grafted.
- Rootstock: The base onto which the scion is grafted.
Choose compatible cuttings, such as grafting apple trees onto other apple trees. Familiarize yourself with plant tissue structure, including the cuticle, bark, wood, and pith. The cambium layer is crucial for successful joining.
Grafting Techniques
- Copulation: Best for similar thicknesses of scion and rootstock. Create 3 cm long mature braids, press them together, and secure with soft twine, treating with garden wax. Ensure there’s a bud on one side and a couple above.
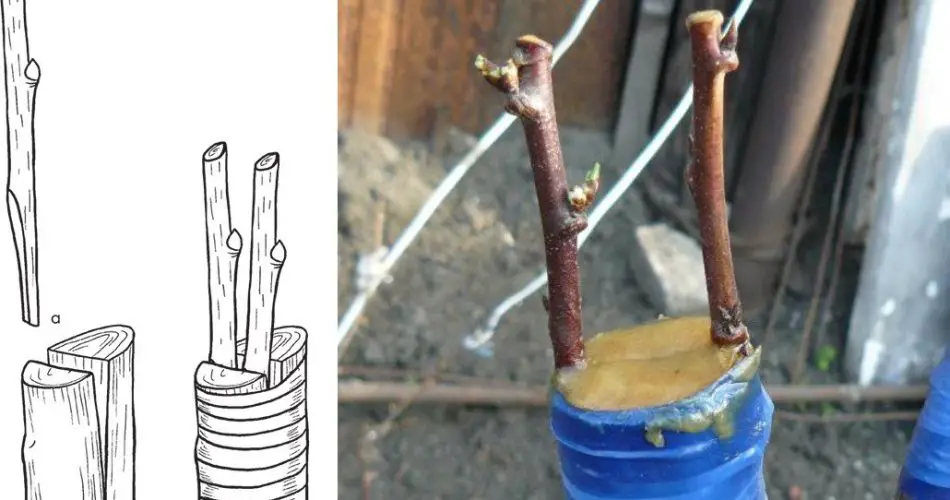
- Improved Copulation: Make longitudinal cuts on the sections and place three or four cuttings inside. Tie them tightly and treat with garden compost.
- Bark Grafting: In May, during sap movement, carefully lift the bark, insert the stem, and secure it.
Caring for Grafts
- Treat all grafting straps with garden varnish or oil paint.
- Process all sections except for the buds.
- Use transparent caps made from film for inspection without moisture exposure.
Tips for Successful Grafting
- Choose the right time for grafting.
- Use a sterile, sharp instrument to make cuts.
- Protect sections from moisture and dust.
- Wrap cuts tightly and process them for pest protection.
- Maintain moisture and provide proper nutrients.
If you graft two cuttings, keep the strongest one. Once it reaches 18 cm, you can graft the top. In July or the following spring, cut back as needed. In the next year, shorten the shoots by one-third to encourage branching.
By following these steps, you can successfully graft trees and enjoy a diverse and fruitful garden!