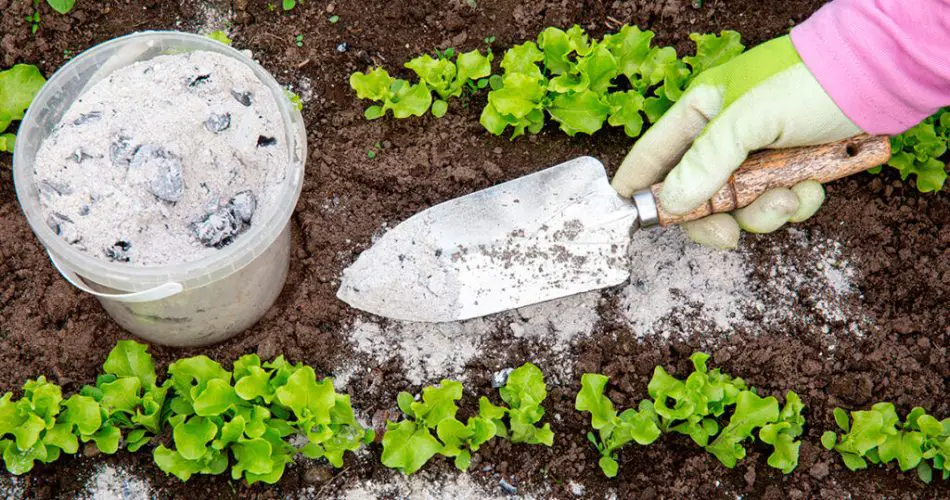
Wood ash is an effective fertilizer packed with essential elements such as potassium, phosphorus, calcium, sodium, magnesium, zinc, copper, and sulfur. Many gardeners utilize it to nourish their plants. However, not all plants can tolerate ash, and some may even suffer or die from its application.
Practical Tips for Using Wood Ash as Fertilizer
Wood ash serves as a universal fertilizer suitable for all soil types and vegetables. It is a cost-effective option that can remain effective in the soil for up to four years. To successfully use ash as fertilizer, it’s crucial to know the appropriate dosage and timing for application. Additionally, be aware of plants that may be sensitive to ash and apply it with caution.
Beneficial Properties of Ash as Fertilizer
Wood ash offers numerous beneficial properties, one of which is soil deoxidation. Even peat soil becomes more conducive to plant growth with the addition of ash. The potassium in wood ash strengthens plant stems, enhancing their resistance to extreme temperatures and diseases. Potassium is also vital for photosynthesis.
Harmful Effects of Ash as Fertilizer
It’s important to note that ash should not be used as fertilizer for acidophilic plants that thrive in acidic environments. Examples of such plants include spruce, azalea, camellia, hydrangea, magnolia, blueberry, cranberry, and bilberry.